Governance Model for Managing Robotics Process Automation (RPA)
As a next step from our last article on creating and managing COE for RPA, next logical question is about having a governance mode for managing RPA initiatives.
The Forrester Institute forecasts the RPA Market Will Reach $2.9 Billion By 2021 and number of BOTS to grow 4 million. The rapid increase of this estimate becomes a management problem for organizations. For those responsible in their organization, ensuring that RPA is implemented and maintained properly is essential to maintain the continuous delivery of value that RPA was designed to bring. The success of scaling up RPA lies in effective governance, risk and control program.
The development of the concept has raised questions like “How to handle the maintenance of hundreds of software robots? What action will be taken if the bot stops? How to keep the software robot running during the change of the IT landscape and regulations?”
Furthermore, as the initiatives of applying RPA grow, complexity and ambiguity will also increase. Notably, today, RPA robots have drastically become widespread and are often seen in a scale up stage in organizations (Deloitte, 2018). RPA can be integrated with machine learning, cognitive technologies and will become more advanced in the future. Consequently, it becomes even harder to manage RPA within the organization. Those management issues and risks related to RPA requires some sort of guidance, for example, it can be done through proper governance, which can mitigate risks that can handle these complexities and ambiguities.
The governance of RPA is needed to ensure secure and safe operation of deployed robots and that these deployments will not result in any breaches of regulations. Besides, software robots deployed without governance can be inefficient and most likely will be costly and burdensome. Governance is a critical tool for the evolution of software bots. The governance of RPA in the field are opportunities for information technologies to create new knowledge and model. Moreover, there is a need to solve this problem because it has not just impact in the present, but also will have significant relevance in the future.
As it can be observed from the model below, the main cycle is located on the top of the diagram and it represents the agile workflow of receiving requests and delivering according to service that has been practiced in the organization. It starts with an incoming request (demand) for the automation of the processes with a software robot from the business or different departments.
RPA Governance Model:
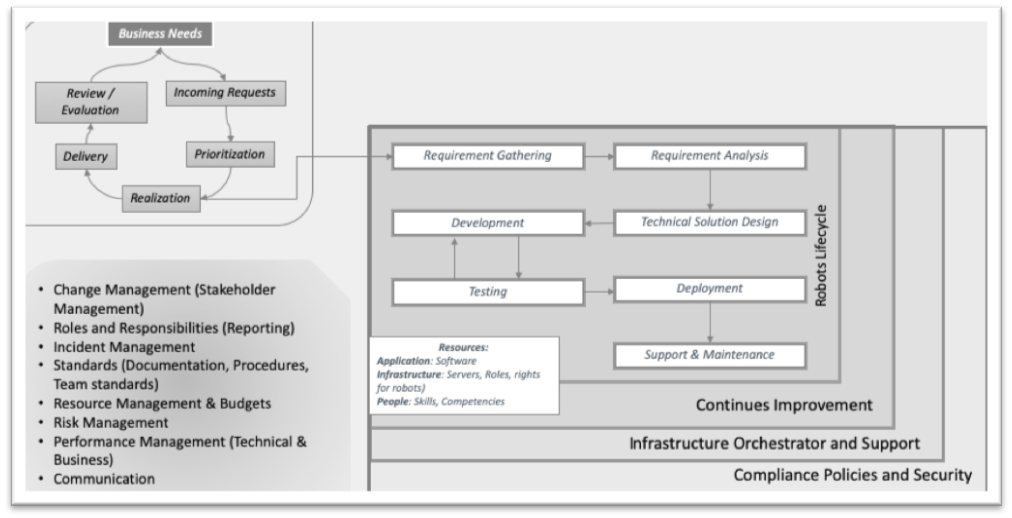
Main Cycle
Incoming requests. The incoming requests appear in demand for business needs. This list of requests can be considered as a backlog
Decision-making (Prioritization). Once the decision is made, it is important to choose a part of the processes which are stable and do not present technological challenges.
Realization. This part focuses on iterative development and incremental improvement of the developed robots as a part of Agile development approach the realization steps are derived from the implementation methodology SDLC best practices.
Requirement gathering: At this stage, all the requirements for the entire process need to be determined. Sometimes it can be called user stories, and this step can be confused with incoming requests. The identification of these problems and activities are being analyzed and documented.
Analysis: At this stage, the analysis of the process automation and feasibility of the study is done in more details.
Solution design: A specific document is studied at the previous stage in order to make the solution design. Formulation design for a future state is done in this stage.
Development: The output of the solution design is the input of the development. The development of the software robot can be divided into modules/units for different developers and actual BOT development is started.
Testing: All developed modules will undergo testing. Errors and failures are corrected so that the robots work properly. User acceptance testing is important to be able to “go live” and then sign off in the later stage.
Deployment: After successfully passing all testing processes, the software robotics process is deployed and released into the business environment. Some monitoring of software bots can happen after the deployment (so-called Hypercare phase) to ensure the proper execution.
Ongoing support & maintenance and operational excellence: Providing ongoing supervision, constant monitoring and maintenance. It is important because software robots are vulnerable to problems when the underlying business processes, application or interfaces change.
External layers:
Infrastructure and Support. IT Infrastructure ensures the platform for RPA runs on scalable and secure hardware, servers and the environments are backed up and runs similar to other enterprise technology services.
Compliance. Compliance means that the solutions are configured and applied in conformation with regulatory requirements, security is appropriate and data is held in an appropriate way. The output data for the designed software robot should be stored for regulatory compliance in a desired format. Security control needs to be altered for robots. Risk management also need to be incorporated and considered everywhere.
Conclusion
The RPA governance model has elements of an IT infrastructure, support services, code management, incident management and more in order to support implementation, maintenance and management of software robots. From the process management perspective, elements such as communication, people change management, assigning responsibilities, assess and control mechanisms for process and other are adopted from relevant concepts of business process management governance.
Consulting team at Luceats is all geared up to answer any of your questions, provide recommendations to ensure you and your organization reaches RPA maturity. Please feel free to reach out to us at [email protected].



Awesome post! Keep up the great work! 🙂